Information systems security – C845 is a comprehensive exploration of the critical field of cybersecurity. It delves into the intricacies of safeguarding information systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
As technology advances and our reliance on digital systems grows, so does the need for robust information security measures. This course equips students with the knowledge and skills necessary to protect sensitive data, maintain system integrity, and ensure business continuity in the face of evolving cyber threats.
Information Systems Security Overview

Information systems security refers to the practices and techniques implemented to protect information systems and their associated data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
Information systems security is crucial because it safeguards sensitive information, ensures the integrity and availability of data, and maintains the confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA) triad. By protecting information systems, organizations can mitigate risks, comply with regulations, and maintain their reputation.
Threats to Information Systems Security
Information systems security faces various threats, including:
- Malware:Malicious software, such as viruses, worms, and ransomware, that can damage or steal data.
- Hackers:Individuals who exploit vulnerabilities in systems to gain unauthorized access and compromise data.
- Social engineering:Techniques used to manipulate individuals into revealing sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security.
- Insider threats:Unauthorized actions by authorized users who have legitimate access to systems.
- Natural disasters and accidents:Events such as earthquakes, floods, or power outages that can disrupt or destroy information systems.
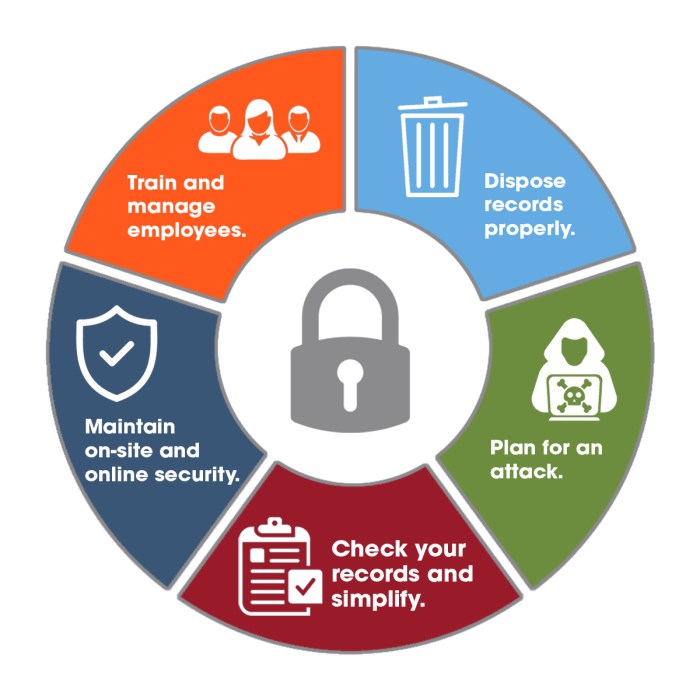
Information Systems Security Controls
Information systems security controls are measures taken to protect information systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
There are three main types of information systems security controls: preventive, detective, and corrective.
Preventive Controls
- Access control: Restricting access to information systems and data to authorized users only.
- Encryption: Converting data into an unreadable format to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Firewalls: Network security devices that monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic.
- Intrusion detection systems: Software that monitors network traffic for suspicious activity.
Detective Controls
- Auditing: Regularly reviewing information systems and data to identify security breaches or vulnerabilities.
- Logging: Recording events and activities within information systems for later analysis.
- Security information and event management (SIEM) systems: Software that collects and analyzes security data from multiple sources.
Corrective Controls
- Backup and recovery: Regularly backing up data and systems to ensure they can be restored in the event of a security breach.
- Incident response plans: Outlining the steps to be taken in the event of a security breach.
- Disaster recovery plans: Outlining the steps to be taken in the event of a major disaster that affects information systems.
The effectiveness of information systems security controls depends on several factors, including the type of control, the level of implementation, and the resources available to implement and maintain the controls.
Information Systems Security Risk Management

Information systems security risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks to information systems. It is a critical part of information systems security, as it helps to ensure that systems are protected from threats and vulnerabilities.Information systems security risk management is important because it helps organizations to:
- Protect their data and systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
- Comply with laws and regulations that require organizations to protect personal information and other sensitive data.
- Reduce the financial impact of security breaches.
- Improve the reputation of the organization.
The steps involved in information systems security risk management include:
Risk Identification
- Identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities to information systems.
- Analyzing the likelihood and impact of each threat and vulnerability.
Risk Assessment
- Evaluating the severity of each risk.
- Prioritizing risks based on their severity.
Risk Mitigation
- Developing and implementing strategies to mitigate each risk.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies.
Information Systems Security Incident Response

Information systems security incident response (ISSIR) is a set of procedures and actions taken in response to a security incident involving information systems. It aims to mitigate the impact of the incident, restore normal operations, and prevent future occurrences.ISSIR is crucial because it helps organizations quickly and effectively respond to security breaches, minimizing damage and protecting sensitive data.
It ensures that incidents are handled in a structured and timely manner, reducing the likelihood of further exploitation and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Steps Involved in ISSIR, Information systems security – c845
ISSIR typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation:Establish a comprehensive ISSIR plan, including roles and responsibilities, communication channels, and incident response procedures.
- Detection and Analysis:Identify and analyze potential security incidents through monitoring systems, intrusion detection, and threat intelligence.
- Containment:Limit the spread and impact of the incident by isolating affected systems, blocking access to compromised accounts, and implementing security controls.
- Eradication:Remove the root cause of the incident by identifying and eliminating malicious software, vulnerabilities, or unauthorized access.
- Recovery:Restore affected systems to normal operation, including restoring data, reconfiguring systems, and implementing additional security measures.
- Lessons Learned:Conduct a post-incident review to identify areas for improvement in ISSIR processes and enhance overall security posture.
Information Systems Security Best Practices: Information Systems Security – C845

Information systems security best practices are a set of guidelines and recommendations that organizations can follow to protect their information systems from threats and vulnerabilities. These best practices are based on industry standards and proven techniques that have been shown to be effective in reducing the risk of security breaches.
Following information systems security best practices can provide organizations with a number of benefits, including:
- Reduced risk of security breaches
- Improved compliance with regulatory requirements
- Increased customer confidence
- Improved business reputation
- Reduced costs associated with security breaches
However, implementing information systems security best practices can also be challenging. Some of the challenges organizations may face include:
- Cost
- Complexity
- Lack of expertise
- Resistance from users
- Changing technology landscape
Despite the challenges, organizations should make every effort to implement information systems security best practices. By doing so, they can significantly reduce the risk of security breaches and protect their valuable data.
Examples of Information Systems Security Best Practices
There are many different information systems security best practices that organizations can follow. Some of the most common include:
- Use strong passwords
- Enable two-factor authentication
- Install and maintain security software
- Back up data regularly
- Educate users about security risks
- Monitor systems for suspicious activity
- Have a plan in place for responding to security breaches
By following these best practices, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of security breaches and protect their valuable data.
FAQ Summary
What is the importance of information systems security?
Information systems security is essential for protecting sensitive data, maintaining system integrity, ensuring business continuity, and complying with regulatory requirements.
What are the different types of information systems security controls?
Information systems security controls can be categorized into three main types: preventive, detective, and corrective. Preventive controls aim to prevent security breaches, detective controls detect and identify breaches, and corrective controls mitigate the impact of breaches.
What is the process of information systems security risk management?
Information systems security risk management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks to information systems. It includes steps such as risk identification, risk assessment, risk mitigation, and risk monitoring.