The concept of “take on a joint liability crossword” encapsulates the intricate legal implications of assuming shared financial obligations. As we delve into this topic, we will explore the various types of joint liability, their advantages and disadvantages, and the crucial considerations one must make before entering into such agreements.
Our discussion will be guided by a thorough examination of legal protections and remedies available to parties involved in joint liability.
Definition and Meaning: Take On A Joint Liability Crossword
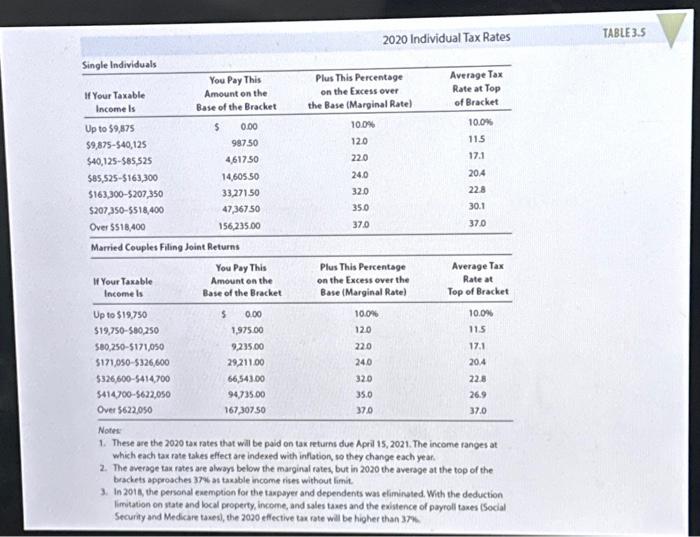
Joint liability, a legal concept, refers to a situation where two or more individuals or entities share responsibility for a debt or obligation. In such arrangements, each party is held fully accountable for the entire debt, regardless of their respective contributions or level of involvement.
Taking on joint liability carries significant legal implications. All parties involved become equally liable for fulfilling the obligation, meaning that any one of them can be held responsible for the entire debt. This can have severe financial consequences, especially if one party fails to meet their obligations.
Examples of Joint Liability
Joint liability commonly arises in various situations, including:
- Co-signing a loan:When two or more individuals co-sign a loan agreement, they become jointly liable for repaying the borrowed amount. If one co-signer defaults on their payments, the other co-signer is legally obligated to cover the outstanding balance.
- Partnership agreements:In partnerships, all partners are jointly liable for the debts and obligations incurred by the partnership. This means that creditors can pursue any partner to satisfy the partnership’s financial obligations.
- Marital debt:In some jurisdictions, spouses may be held jointly liable for debts incurred during their marriage. This can include mortgages, credit card bills, and other financial obligations.
Types of Joint Liability

Joint liability arises when multiple parties are legally responsible for the same obligation. There are several types of joint liability, each with its own implications for the parties involved.
Joint and Several Liability
In joint and several liability, each party is fully liable for the entire obligation. This means that the creditor can pursue any one of the parties for the full amount of the debt, regardless of the other parties’ contributions.
Joint and Several Liability with Contribution
Joint and several liability with contribution is similar to joint and several liability, but with one key difference. In this type of liability, the parties have a right to contribution from each other. This means that if one party pays more than their share of the obligation, they can seek reimbursement from the other parties.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Taking on joint liability offers certain advantages and disadvantages that should be carefully considered before entering into such an agreement. Understanding these implications can help individuals make informed decisions and manage their financial obligations effectively.
Advantages, Take on a joint liability crossword
Joint liability provides several advantages, including:
- Increased access to credit:By combining incomes and credit histories, joint applicants may qualify for larger loans or better interest rates than they could individually.
- Shared risk:In the event of a default, the burden of debt is shared among the co-borrowers, reducing the financial impact on any one individual.
Disadvantages
However, joint liability also carries potential disadvantages:
- Increased exposure to debt:Each co-borrower is fully responsible for the entire debt, even if they did not personally incur it. This can lead to financial hardship if one party fails to fulfill their obligations.
- Potential for disputes:Joint liability can create tension and conflict among co-borrowers, especially if there are disagreements about financial decisions or repayment responsibilities.
For example, consider a couple who takes out a joint mortgage. If one spouse loses their job and is unable to contribute to the mortgage payments, the other spouse is legally obligated to cover the full amount. This could strain their relationship and potentially lead to financial distress.
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to take on joint liability should be based on a careful assessment of the potential benefits and risks involved. Individuals should consider their financial situation, their relationship with the other parties, and their ability to manage the responsibilities associated with joint liability.
Considerations Before Taking on Joint Liability
Before assuming joint liability, it is crucial to carefully consider various factors. These include assessing the creditworthiness of the other parties involved, thoroughly reviewing the terms of the agreement, and understanding the potential consequences of such an undertaking.
To assess the risks and benefits of taking on joint liability, one must evaluate the financial stability and reliability of the other parties. This includes examining their credit history, income, and assets. Additionally, it is essential to carefully review the terms of the agreement, paying particular attention to the specific obligations and responsibilities of each party.
Understanding the potential consequences of default or breach of contract is also paramount.
Negotiating Joint Liability Agreements
When negotiating joint liability agreements, it is advisable to seek professional legal advice to ensure that the terms are fair and equitable for all parties involved. It is important to clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each party, as well as the consequences of default or breach of contract.
Additionally, it is crucial to consider the potential impact of joint liability on personal finances and creditworthiness.
Legal Protections and Remedies

Individuals who assume joint liability are entitled to specific legal protections and remedies to safeguard their interests. These safeguards are crucial in ensuring equitable distribution of obligations and providing avenues for recourse in the event of disputes or defaults.
Right to Contribution
The right to contribution allows a party who has fulfilled more than their share of a joint obligation to seek reimbursement from other jointly liable parties. This right ensures that the burden of the obligation is shared fairly among all parties.
Right to Indemnity
The right to indemnity grants a party who has been held liable for the entire joint obligation the right to recover the full amount from other jointly liable parties. This remedy is typically available when one party is primarily responsible for the breach of contract or other legal duty that gave rise to the obligation.
Payment
Payment is the most common remedy for breach of a joint obligation. When a joint obligation becomes due, any of the jointly liable parties may be required to pay the full amount. Once the obligation is satisfied, the party who made the payment can seek contribution or indemnity from the other jointly liable parties.
Foreclosure
In cases involving secured joint obligations, such as mortgages, foreclosure may be used as a remedy. If a jointly liable party defaults on their payment obligations, the lender may foreclose on the property securing the loan. The proceeds from the foreclosure sale are then used to satisfy the outstanding debt.
Garnishment
Garnishment is a legal process that allows a creditor to seize a portion of a debtor’s wages or other income to satisfy a joint obligation. This remedy is typically used when other collection efforts have been unsuccessful.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the different types of joint liability?
Joint liability can be categorized into joint and several liability, where each party is fully liable for the entire debt, and joint and several liability with contribution, where parties share the responsibility for the debt but can seek contribution from other liable parties.
What are the advantages of taking on joint liability?
Joint liability can provide increased access to credit, particularly for individuals with limited credit history or low credit scores. It can also facilitate shared risk, as multiple parties assume the financial burden.
What are the disadvantages of taking on joint liability?
Joint liability exposes individuals to increased debt exposure, as they are responsible for the entire debt, regardless of the actions or financial circumstances of other liable parties. Additionally, joint liability can lead to disputes among parties, particularly in situations where one party fails to fulfill their obligations.