Cell transport amoeba sisters answer key – Embark on a journey into the realm of cell transport in amoeba sisters, where the intricate mechanisms of cellular life unfold. This definitive guide delves into the fundamental processes that govern the movement of molecules and substances across cell membranes, illuminating the vital role of cell transport in the survival and interactions of these fascinating microorganisms.
From passive diffusion to active transport, we explore the diverse methods employed by amoeba sisters to transport essential nutrients, eliminate waste products, and maintain cellular homeostasis. Along the way, we uncover the applications of cell transport in research, medicine, and industry, showcasing its profound impact on our understanding of biology and its practical implications.
Cell Transport in Amoeba Sisters
Amoeba sisters are single-celled organisms that use various mechanisms for cell transport. Cell transport is the movement of molecules and substances across the cell membrane, which is essential for the cell’s survival and function.
Types of Cell Transport
- Passive Transport:Movement of molecules across the cell membrane without the use of energy. Examples include diffusion and osmosis.
- Active Transport:Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient, requiring energy from ATP. Examples include the sodium-potassium pump and endocytosis.
Examples of Cell Transport in Amoeba Sisters, Cell transport amoeba sisters answer key
- Diffusion:Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration. Amoeba sisters use diffusion to take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide.
- Endocytosis:The process by which amoeba sisters engulf food particles. The cell membrane folds inward, forming a vesicle that surrounds the food.
- Exocytosis:The process by which amoeba sisters release waste products. The cell membrane fuses with a vesicle containing the waste, releasing its contents outside the cell.
Methods of Cell Transport: Cell Transport Amoeba Sisters Answer Key
Passive Transport
Passive transport occurs without the use of energy. Molecules move from an area of high concentration to low concentration, down their concentration gradient.
- Diffusion:Movement of molecules through the cell membrane without the need for carrier proteins.
- Osmosis:Movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to low water concentration.
Active Transport
Active transport requires energy to move molecules against their concentration gradient. Carrier proteins in the cell membrane bind to molecules and transport them across the membrane.
- Sodium-Potassium Pump:Maintains the cell’s electrochemical gradient by actively transporting sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell.
- Endocytosis:The process by which the cell membrane engulfs large molecules or particles, forming a vesicle.
- Exocytosis:The process by which the cell membrane fuses with a vesicle, releasing its contents outside the cell.
| Method | Mechanism |
|---|---|
| Diffusion | Movement of molecules down a concentration gradient without the use of energy. |
| Osmosis | Movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from high to low water concentration. |
| Sodium-Potassium Pump | Active transport of sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell, maintaining the cell’s electrochemical gradient. |
| Endocytosis | Engulfing of large molecules or particles by the cell membrane, forming a vesicle. |
| Exocytosis | Fusion of the cell membrane with a vesicle, releasing its contents outside the cell. |
Importance of Cell Transport
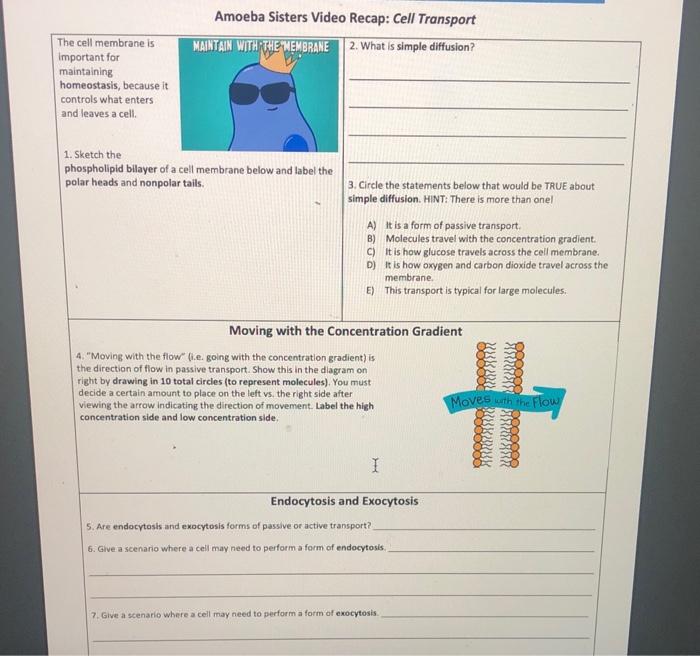
Cell transport is essential for the survival and function of amoeba sisters. It allows the cell to:
- Take in nutrients:Amoeba sisters use endocytosis to engulf food particles, providing them with the energy and building blocks they need.
- Expel waste products:Amoeba sisters use exocytosis to release waste products, preventing their accumulation in the cell.
- Maintain homeostasis:Cell transport helps maintain the cell’s internal environment, including pH and ion concentrations.
- Interact with the environment:Amoeba sisters use cell transport to exchange molecules with their surroundings, allowing them to respond to changes in the environment.
Applications of Cell Transport

Cell transport has various applications in research, medicine, and industry:
Research
- Studying cell biology:Cell transport is essential for understanding how cells function and interact with each other.
- Developing new drugs:Cell transport can be targeted by drugs to improve drug delivery and efficacy.
Medicine
- Treating diseases:Cell transport can be manipulated to treat diseases such as cancer and cystic fibrosis.
- Gene therapy:Cell transport can be used to deliver genes into cells for therapeutic purposes.
Industry
- Biotechnology:Cell transport is used in the production of proteins and other biomolecules.
- Environmental science:Cell transport is studied to understand the uptake and release of pollutants by organisms.
Clarifying Questions
What is the significance of cell transport in amoeba sisters?
Cell transport is essential for the survival of amoeba sisters as it enables them to acquire nutrients, eliminate waste, and maintain their internal environment.
How does passive diffusion contribute to cell transport in amoeba sisters?
Passive diffusion allows molecules to move across cell membranes without the expenditure of energy, facilitating the exchange of substances between the cell and its surroundings.
What is the role of active transport in cell transport in amoeba sisters?
Active transport utilizes energy to move molecules against their concentration gradient, ensuring the uptake of essential nutrients and the removal of waste products.
