Mount pinatubo and the ring of fire answer key – Embark on a scientific odyssey with our comprehensive exploration of Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire. This in-depth analysis unravels the geological tapestry of one of the world’s most iconic volcanoes, examining its profound impact and the intricate workings of plate tectonics that shape our planet.
Mount Pinatubo’s catastrophic eruption in 1991 serves as a poignant case study, showcasing the devastating power of volcanic forces and the resilience of human communities. As we delve into the Ring of Fire, we uncover the complex interplay between subduction zones, volcanic activity, and earthquake occurrences, revealing the dynamic nature of our planet’s crust.
Mount Pinatubo and its Impact

Mount Pinatubo, located in the Philippines, is an active stratovolcano known for its catastrophic eruption in 1991. This eruption was one of the largest in recorded history, with a Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) of 6.
The 1991 Eruption
The eruption of Mount Pinatubo on June 15, 1991, released an estimated 10 cubic kilometers of volcanic ash into the atmosphere, creating a column that reached a height of 35 kilometers. The ash cloud spread across the globe, causing widespread disruption to air travel and communication.
The eruption also triggered pyroclastic flows and lahars (mudflows), which devastated surrounding areas.
Long-Term Global Impact
The eruption of Mount Pinatubo had a significant impact on the global climate. The ash cloud reflected sunlight back into space, causing a temporary decrease in global temperatures by about 0.5 degrees Celsius. The eruption also released large amounts of sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere, which contributed to the formation of acid rain.
Local Impact and Mitigation
The eruption of Mount Pinatubo had a devastating impact on the local population. Thousands of people were killed or injured, and millions were displaced from their homes. The Philippine government implemented a massive relief effort, including evacuation plans and the provision of food and shelter to those affected.
The Ring of Fire and Plate Tectonics: Mount Pinatubo And The Ring Of Fire Answer Key
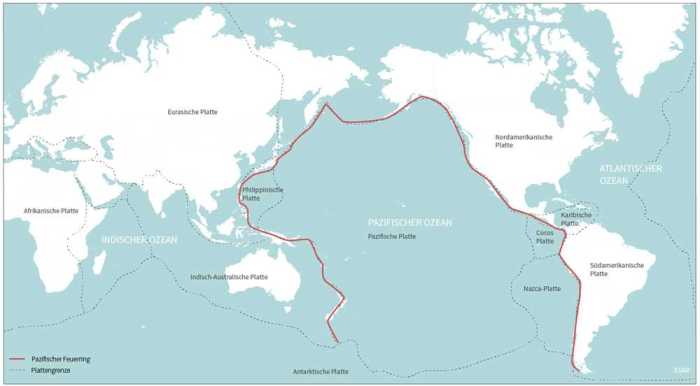
The Ring of Fire is a horseshoe-shaped region around the Pacific Ocean that is characterized by a high level of seismic and volcanic activity. This region is home to about 75% of the world’s volcanoes and is responsible for about 90% of the world’s earthquakes.
Geological Formation, Mount pinatubo and the ring of fire answer key
The Ring of Fire is the result of the interaction between the Pacific Plate and the surrounding tectonic plates. As the Pacific Plate moves beneath the other plates, it melts and rises to the surface, forming volcanoes. The subduction of the Pacific Plate also creates areas of high pressure and temperature, which can lead to earthquakes.
Other Significant Volcanic Eruptions
In addition to Mount Pinatubo, there have been several other significant volcanic eruptions in the Ring of Fire, including the 1883 eruption of Krakatoa in Indonesia and the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens in the United States.
Volcanic Hazards and Mitigation Strategies

Volcanic eruptions can pose a significant threat to human life and property. The main hazards associated with volcanic eruptions include:
- Ashfall: Ashfall can block sunlight, disrupt transportation, and contaminate water supplies.
- Pyroclastic flows: Pyroclastic flows are fast-moving clouds of hot gas and ash that can travel at speeds of up to 700 kilometers per hour.
- Lahars: Lahars are mudflows that are formed when volcanic ash mixes with water.
- Volcanic gases: Volcanic gases, such as sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide, can be harmful to human health.
There are a number of strategies that can be used to mitigate volcanic hazards, including:
- Volcanic monitoring: Volcanic monitoring can help to identify volcanoes that are at risk of erupting.
- Early warning systems: Early warning systems can provide people with time to evacuate before an eruption occurs.
- Evacuation plans: Evacuation plans can help to ensure that people know what to do in the event of an eruption.
- Protective measures: Protective measures, such as masks and respirators, can help to protect people from the effects of volcanic ash and gases.
Scientific Research and Technological Advancements

The eruption of Mount Pinatubo was a major scientific event that has led to a number of important advances in our understanding of volcanic processes. Scientists have studied the eruption to learn more about the causes of volcanic eruptions, the effects of volcanic ash on the atmosphere, and the long-term impact of volcanic eruptions on the environment.
Technological advancements have also played a major role in improving our ability to monitor and predict volcanic eruptions. These advancements include the development of new seismic monitoring techniques, satellite-based remote sensing, and computer modeling.
These advancements have helped us to better understand volcanic processes and to develop more effective strategies for mitigating volcanic hazards.
FAQ Resource
What is the significance of the 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo?
The 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo was one of the largest volcanic eruptions of the 20th century, releasing vast amounts of ash and sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere. It had a profound impact on global climate, causing a temporary cooling effect and affecting weather patterns worldwide.
How does the Ring of Fire relate to plate tectonics?
The Ring of Fire is a horseshoe-shaped region around the Pacific Ocean where a majority of the world’s earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur. It is formed by the convergence of tectonic plates, where one plate subducts beneath another, creating areas of intense geological activity.
What are the primary hazards associated with volcanic eruptions?
Volcanic eruptions can pose various hazards, including ashfall, pyroclastic flows, lahars (mudflows), and volcanic gases. These hazards can cause significant damage to infrastructure, agriculture, and human health.
How do scientists monitor volcanic activity?
Scientists use a variety of techniques to monitor volcanic activity, including seismic monitoring, gas emissions analysis, and satellite imagery. These methods help identify potential eruptions and provide early warnings to nearby communities.
What are the strategies for mitigating volcanic hazards?
Mitigating volcanic hazards involves implementing early warning systems, evacuation plans, and protective measures. These strategies aim to reduce the risk to human life and property by providing timely information and enabling communities to prepare for potential eruptions.