Welcome to the realm of phospholipid and membrane transport, where the intricate dance of molecules orchestrates the vital processes of life. Dive into the depths of this captivating topic as we unlock the secrets of the phospholipid and membrane transport kit answer key, a treasure trove of knowledge that empowers you to decipher the mechanisms that govern cell transport.
Within the confines of this comprehensive guide, we embark on a journey to unravel the enigmatic structure and functions of phospholipids, the building blocks of cell membranes. We delve into the diverse mechanisms of membrane transport, exploring their significance in maintaining cellular homeostasis and facilitating communication between cells.
1. Phospholipid Structure and Function
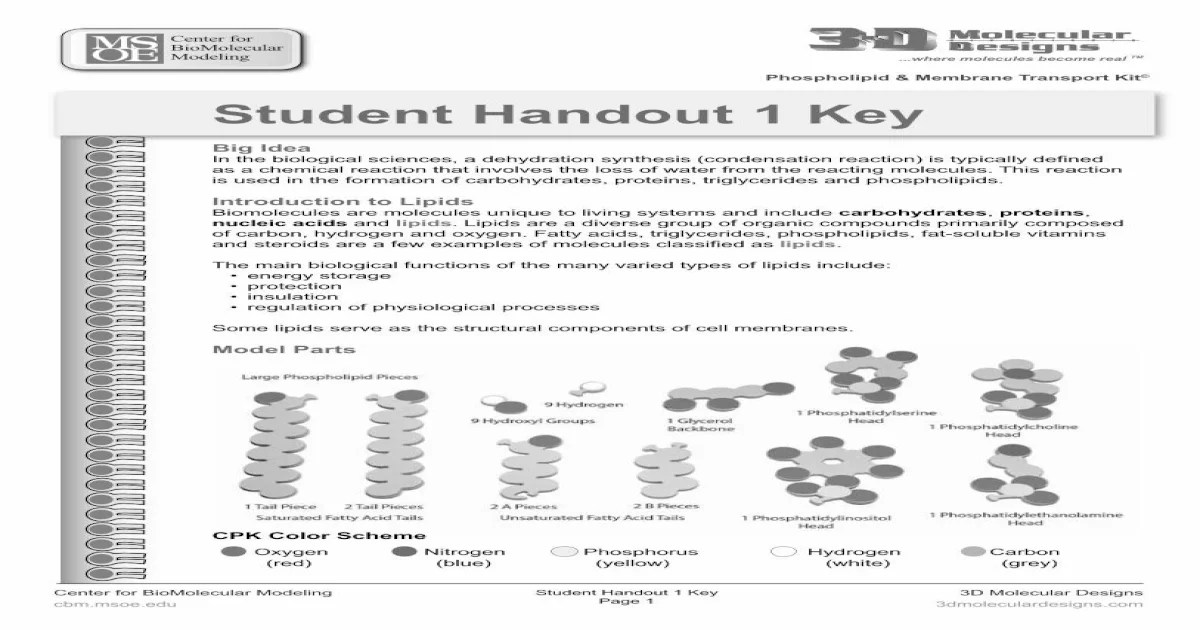
Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules, meaning they have both hydrophilic (water-loving) and hydrophobic (water-hating) regions. The hydrophilic region consists of a phosphate group and a glycerol molecule, while the hydrophobic region consists of two fatty acid chains.
Phospholipids are the main components of cell membranes. They form a bilayer, with the hydrophilic regions facing outward and the hydrophobic regions facing inward. This bilayer creates a barrier that separates the inside of the cell from the outside environment.
There are many different types of phospholipids, each with its own unique function. For example, phosphatidylcholine is the most common phospholipid in animal cell membranes, while phosphatidylethanolamine is the most common phospholipid in plant cell membranes.
2. Membrane Transport
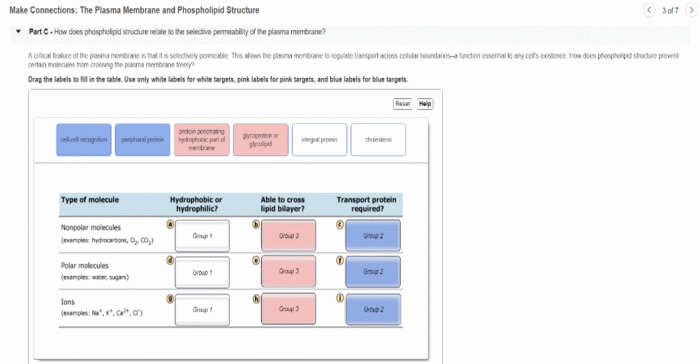
Membrane transport is the movement of molecules across cell membranes. It is essential for cells to survive, as it allows them to take in nutrients and expel waste products.
There are two main types of membrane transport mechanisms: passive transport and active transport.
- Passive transport is the movement of molecules down their concentration gradient, from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This type of transport does not require energy.
- Active transport is the movement of molecules against their concentration gradient, from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. This type of transport requires energy.
Membrane transport is used in a variety of biological processes, including nutrient uptake, waste removal, and cell signaling.
3. Phospholipid and Membrane Transport Kit
A phospholipid and membrane transport kit is a set of materials that can be used to demonstrate membrane transport processes. The kit typically includes a phospholipid bilayer, a variety of solutes, and a way to measure the movement of solutes across the bilayer.
The phospholipid and membrane transport kit can be used to demonstrate a variety of membrane transport processes, including passive transport, active transport, and facilitated diffusion.
4. Experimental Design and Data Analysis

To design an experiment using the phospholipid and membrane transport kit, you will need to decide which membrane transport process you want to investigate. Once you have decided on a process, you will need to design an experiment that will allow you to measure the movement of solutes across the bilayer.
Once you have collected your data, you will need to analyze it to determine the rate of solute movement. You can use this information to calculate the permeability of the bilayer to the solute.
5. Applications and Implications
Membrane transport research has a wide range of applications in medicine, biotechnology, and other fields.
- In medicine, membrane transport research is used to develop new drugs that can target specific cells or tissues.
- In biotechnology, membrane transport research is used to develop new ways to produce biofuels and other products.
Membrane transport research is also important for understanding cell function and disease. By understanding how molecules move across cell membranes, we can gain insights into how cells work and how diseases develop.
FAQ Resource: Phospholipid And Membrane Transport Kit Answer Key
What is the primary function of phospholipids in cell membranes?
Phospholipids form a lipid bilayer, which serves as a selectively permeable barrier, regulating the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
How does membrane transport facilitate cell communication?
Membrane transport mechanisms enable the exchange of ions, nutrients, and signaling molecules between cells, allowing them to communicate and coordinate their activities.
What is the purpose of using a phospholipid and membrane transport kit?
Phospholipid and membrane transport kits provide a hands-on approach to studying membrane transport processes, allowing students and researchers to visualize and analyze the movement of molecules across lipid bilayers.
